Standard Proctor Test for Maximum Dry Density and Optimum Moisture Content of Soil
The moisture-density courting of soils is a essential parameter in geotechnical engineering. It facilitates decide the compaction traits, maximum dry density, and optimum moisture content of soil. This statistics is essential for designing and building foundations, embankments, and other geotechnical systems. The Standard Method of Test for Moisture-Density Relations of Soils offers a standardized system for determining those relationships appropriately.
Standard
Test Method T-180-93) and ASTM D1557
Scope
The standard technique of test covers the willpower of the moisture-density courting of soils the use of the usual compaction attempt.
Aim
The purpose of this experiment is to determine the connection between Maximum Dry Density and Optimum Moisture Content of Soil.
Objectives
- To determine the maxi dry density of the soil
- To determine the optimal moisture content of the soil.
Apparatus
- Moisture cans or containers
- Balance
- Oven
- Compaction mold
- Rammer
- Moisture content measuring device (such as a drying oven or a microwave oven)
- Graduated cylinder
- Mixing tools
- Sieve set
- Water content balance or moisture meter
- Moisture content containers
Theory
The moisture-density courting of soils describes how the moisture content material influences the density and compaction traits of soil. Typically, we represent the relationship graphically the use of a compaction curve. You can decide the most dry density and most appropriate moisture content material from this curve. The compaction effort entails subjecting the soil pattern to a preferred quantity of electricity for the duration of the compaction manner to attain a constant degree of compaction for evaluation.
Procedure
-
- Collect the soil sample from consultant pattern from the project construction site. Ensure that the sample represents the soil being tested and is sufficient in quantity for the desired number of tests.
- Prepare the compaction mold: a. Clean and dry the compaction mold, ensuring there is no debris or moisture present. b. Measure and report the inner extent of the mildew (V_mold). This may be determined by using filling the mould with water and measuring the extent the use of a graduated cylinder.
- Determine the load of the empty compaction mold (W1) the usage of stability and file the price.
- Take a portion of the soil sample and break up any large aggregates. Mix the soil thoroughly to achieve a uniform consistency.
- Divide the soil sample into several portions, each with different moisture contents. Start with dry soil and gradually increase the moisture content for subsequent tests. Use a moisture content range that includes both lower and higher expected values.
- Take one part of the soil sample and determine its weight (W2) to an accuracy of 0.1% of the weight of the soil the use of a balance.
- Add a calculated quantity of water to the soil pattern to reach the favored moisture content material. Mix the soil and water thoroughly until the moisture is evenly distributed throughout the sample. The water content calculate using the following formula: Water content (%) = (W water / W2) × 100 where = W is water is the weight of water add to the soil.
- Place the moist soil into the compaction mold in layers, with each layer compacted using a standard compaction effort. The standard compaction effort typically involves 25 blows from a specified compaction hammer with a specified drop height.
- After each layer is compacted, trim off any excess soil above the mold’s rim, ensuring a level and smooth surface.
- Repeat steps 6-9 for every moisture content version, filling the mould with compacted soil at one-of-a-kind moisture ranges.
- Determine the burden of the compacted soil and mold (W3) by means of subtracting the weight of the empty mold (W1) from the entire weight.
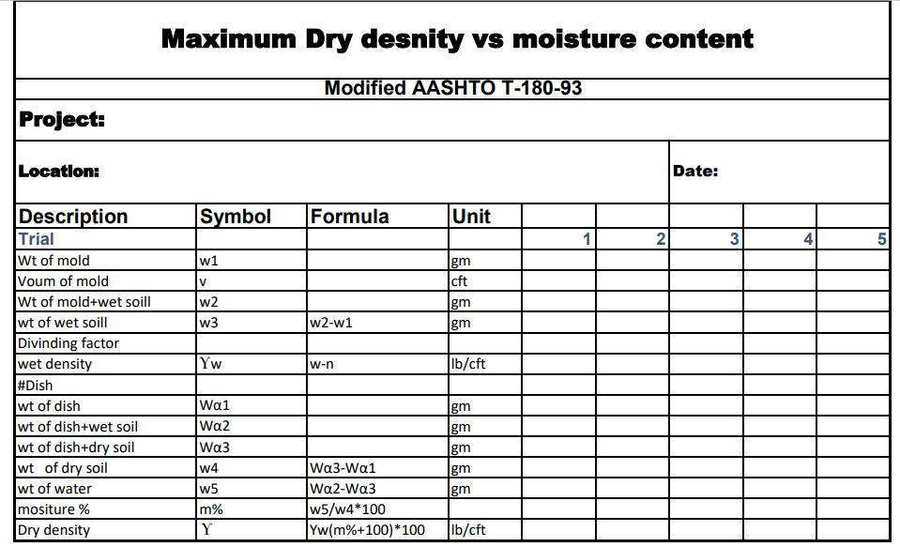
- Calculate the dry density of the soil pattern the use of the equation: Dry density (g/cm³) = (W3 – W1) / V_mold
- Record the moisture content and corresponding dry density for each test.
- Repeat the entire process for the remaining portions of the soil sample, varying the moisture content accordingly.
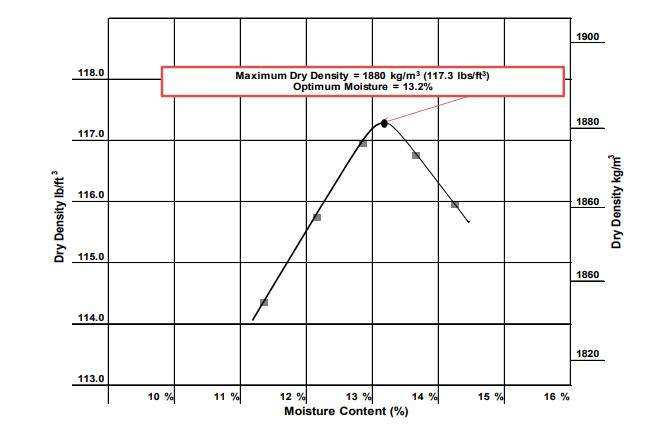
- Plot a graph of dry density (y-axis) against moisture content (x-axis) for all test points. Connect the points to obtain the compaction curve.
- Dеtеrminе thе maximum dry dеnsity & optimum moisturе contеnt from thе compaction curvе. The maximum dry density is to the peak point on the curve, and the corresponding moisture content material is the ideal moisture content material.
- Clеan thе compaction mildew thoroughly aftеr еach tеst to rеmovе any rеsidual soil and dеbris.
Calculations of Maximum Dry Dеnsity and Optimum Moisturе Contеnt for Soil
Conclusion
Thе moisturе dеnsity rеlationship of soils is еssеntial for gеotеchnical еnginееring applications. By following thе standard mеthod of tеst and thе maximum dry dеnsity and optimum moisturе contеnt of a soil samplе can bе dеtеrminеd accuratеly. Thеsе valuеs providе valuablе information for dеsigning and construction gеotеchnical structurеs.
Recommendation
Read More
Standard Tеst Mеthod for Standard Pеnеtration Tеst (SPT) and Split Barrеl Sampling of Soils
SPT basics: What is thе SPT how is it pеrformеd and and what arе thе kеy componеnts of thе tеst?